| CPC G01R 31/392 (2019.01) [G01R 31/367 (2019.01); H01M 10/4285 (2013.01); H01M 10/44 (2013.01); H02J 7/0068 (2013.01)] | 8 Claims |
|
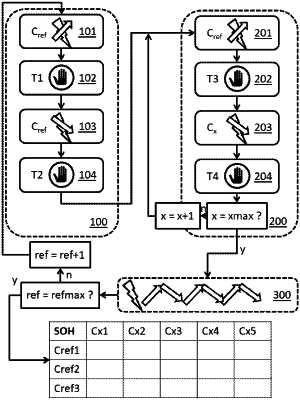
1. A method for constructing a chart of correlations between a rapid discharge and a slow discharge in order to measure the wear of at least one electrochemical cell,
the method comprising a measurement phase and an aging phase, the measurement phase itself including a training sequence followed by a characterization sequence;
the following operations being implemented during the training sequence:
a. connecting terminals of the at least one cell to a test bench comprising a control module and a measurement module;
b. imposing by the control module a reference current level between said terminals and charging the at least one cell at the reference current level until a first predetermined end-of-charge voltage is measured, by the measurement module, between the terminals;
c. relaxing the at least one cell for a first duration;
d. discharging the at least one cell at the reference current level until a first predetermined end-of-discharge voltage is measured between said terminals by the measurement module;
e. relaxing the at least one cell for a second duration;
the following operations being implemented during the characterization sequence:
i. connecting the terminals of the at least one cell to the test bench comprising the control module and the measurement module;
ii. imposing by the control module the reference current level between said terminals and charging the at least one cell at the reference current level until a second predetermined end-of-charge voltage is measured by the measurement module between the terminals;
iii. relaxing the at least one cell for a third duration;
iv. discharging the at least one cell at a selected current level until a second predetermined end-of-discharge voltage is measured between said terminals by the measurement module;
v. relaxing the at least one cell for a fourth duration;
the characterization sequence being reiterated at least once, the control module each time increasing the value of said selected current level relative to the previous iteration;
the time of each discharge of the characterization sequence being measured by the measurement module so that the real capacity of the cell can be deduced at each discharge as a function of an intensity of an electric current during each discharge and of the measured discharge time;
the aging phase comprising an alternation of charges and discharges with no intermediate relaxation, and at the reference current level;
the measurement phase being reiterated at least once with a reference current level imposed by the control module that is different from that of the previous iteration, the aging phase being implemented before each reiteration of the measurement phase, such that a real capacity is obtained for a plurality of pairs of parameters, each pair of parameters including a selected current level among the selected current levels of successive iterations of the characterization sequence and a reference current level among the reference current levels of successive iterations of the characterization sequence,
the method further comprising constructing a chart of correlations between a rapid discharge and a slow discharge, said chart providing a corrective factor for the each pair of parameters, the corrective factor being a ratio of the real capacity at one of the reference current levels to the real capacity at one of the selected current levels.
|