| CPC G01N 30/16 (2013.01) [G01N 30/72 (2013.01); G01N 30/74 (2013.01); G01N 30/8637 (2013.01); G01N 30/06 (2013.01); G01N 2030/027 (2013.01)] | 24 Claims |
|
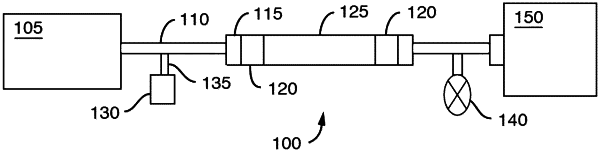
1. A method for evaluating system inertness, the method comprising:
repeatedly injecting a sample into a system, wherein the sample comprises a positive control; the system comprising: fluidic paths wherein interior surfaces of the fluidic paths define wetted surfaces, and wherein at least a portion of the wetted surfaces of the fluidic flow path are coated with an inert coating, and wherein the inert coating is inert to at least one analyte in the sample;
detecting a value associated with the positive control; and
analyzing the values associated with the detected positive control to determine system inertness.
|