| CPC A61B 5/165 (2013.01) [A61B 5/0533 (2013.01); A61B 5/7267 (2013.01); A61B 5/7278 (2013.01); G06N 20/00 (2019.01); G16H 10/60 (2018.01); G16H 40/67 (2018.01); G16H 50/70 (2018.01)] | 8 Claims |
|
1. A processor implemented method for assessment of cognitive load from bio-potentials, comprising:
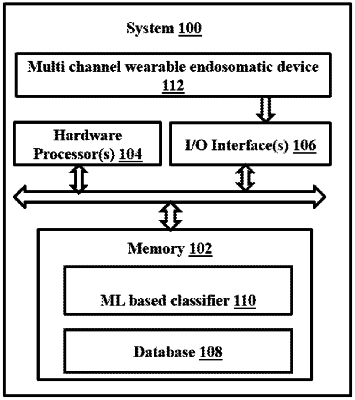
acquiring, via a multichannel wearable endosomatic device by one or more hardware processors, a plurality of bio-potential signals, wherein
the plurality of bio-potential signals provides a task specific data of a subject performing a cognitive task,
the cognitive task including one of a high load task or a low load task, and
the plurality of bio-potential signals is time stamped;
extracting, by the one or more hardware processors, baseline data and task data based on time stamps associated with each of the plurality of bio-potential signals, wherein
the baseline data corresponds to segment of each of the plurality of bio-potential signals when the subject experiences a nil cognitive load during the cognitive task being performed, and
the task data corresponds to segment of each of the plurality of bio-potential signals when the subject experiences an active cognitive load during the cognitive task being performed;
deriving, by the one or more hardware processors, a plurality of deviation signals from the plurality bio-potential signals by:
computing a mean of each of baseline data and the task data; and
subtracting the computed mean from each of the baseline data and the task data;
extracting, by the one or more hardware processors, a plurality of features from the plurality of deviation signals, wherein the plurality of features comprises a statistical set of features and a spectral set of features, wherein the spectral set of features comprises a mean frequency, a power at the mean frequency, a total power, a mean power, a median frequency, a power at median frequency, a peak frequency, a peak power, a signal band-power, a first moment, a second moment, and a third moment;
determining, by the one or more hardware processors, an optimum set of features from the plurality of features wherein the determined set of features best differentiates between the high load task or the low load task; and
training, by the one or more hardware processors, a classifier for classifying the cognitive task into one of the high load task or the low load task using the determined set of features, wherein the determined set of features is labeled as corresponding to the high load task or the low load task.
|