| CPC A61B 3/135 (2013.01) [A61B 3/102 (2013.01)] | 8 Claims |
|
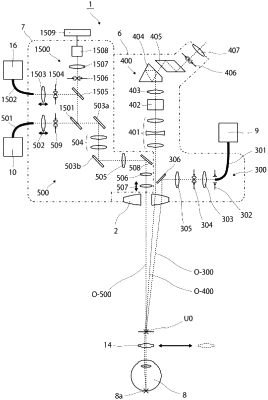
1. An ophthalmologic microscope comprising:
an illuminating optical system for illuminating a subject's eye;
an observation optical system that comprises an observation optical system for left eye and an observation optical system for right eye to observe the subject's eye illuminated by the illuminating optical system;
an objective lens through which an optical axis of the observation optical system for left eye and an optical axis of the observation optical system for right eye of the observation optical system commonly penetrate; and
an OCT optical system for scanning a measuring light to test the subject's eye with Optical Coherence Tomography;
wherein the observation optical system, the objective lens, and the OCT optical system are placed in such a way that the optical axis of the OCT optical system does not penetrate through the objective lens through which the optical axis of the observation optical system penetrates, and the optical axis of the observation optical system and the optical axis of the OCT optical system are non-coaxial; and
further comprising an SLO optical system that scans a light ray which is a visible ray, a near infrared ray, or an infrared ray and guides the light to the subject's eye so as to become substantially coaxial with the optical axis of the OCT optical system, and the SLO optical system being configured such that the ophthalmologic microscope observe an area including a section of the subject's eye where the OCT optical system scans, with the SLO optical system.
|