| CPC H04W 72/1273 (2013.01) [H04L 1/0004 (2013.01); H04W 56/0045 (2013.01); H04W 72/0446 (2013.01); H04W 72/1268 (2013.01); H04W 72/23 (2023.01); H04W 72/535 (2023.01); H04W 80/02 (2013.01)] | 46 Claims |
|
1. An apparatus for wireless communications at a user equipment (UE), comprising:
a memory; and
at least one processor coupled to the memory, wherein the at least one processor is configured to:
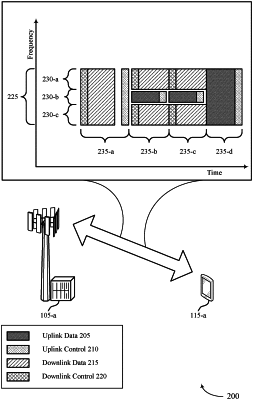
receive a joint control message that comprises scheduling information for a downlink message for the UE and for an uplink shared channel message for transmission by the UE, wherein the scheduling information allocates a first set of resources within a slot for the downlink message and a second set of resources within the slot for the uplink shared channel message such that the first set of resources and the second set of resources at least partially overlap in time or frequency, in accordance with a sub-band full duplex capability of the UE;
receive the downlink message via the first set of resources according to first timing information, wherein the first timing information is based at least in part on the scheduling information; and
transmit the uplink shared channel message via the second set of resources according to second timing information, wherein the second timing information is based at least in part on the first timing information and on the scheduling information.
|