| CPC G06T 7/0014 (2013.01) [G01N 1/30 (2013.01); G01N 33/4833 (2013.01); G01N 2001/302 (2013.01); G06T 2207/10024 (2013.01); G06T 2207/20021 (2013.01); G06T 2207/20081 (2013.01); G06T 2207/30028 (2013.01); G06T 2207/30096 (2013.01)] | 18 Claims |
|
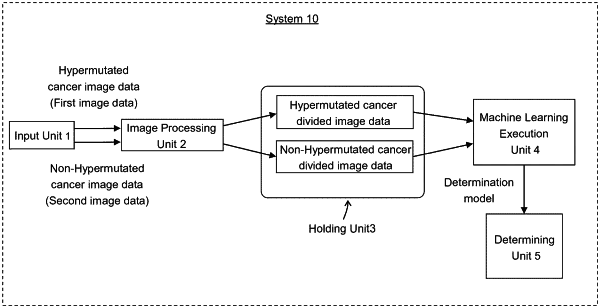
1. A computer system for determining hypermutated cancer comprising one or more computers programmed to perform steps comprising:
inputting a plurality of first image data, a plurality of second image data and a plurality of third image data, wherein
the first image data represents an image of a pathological section of stained hypermutated cancer,
the second image data represents an image of a pathological section of cancer which is not hypermutated, and is stained same as the pathological section of the first image data, and
the third image data represents an image of a pathological section of cancer which is newly determined whether hypermutated or not, and is stained same as the pathological section of the first image data;
holding a first image data and a second image data;
performing a Z value conversion process of the first image data, the second image data and the third image data, converting each RGB color in each pixel into Z value in the CIE color system based on the entire color distribution of the first image data, the second image data and the third image data; and
generating a determination model determining whether a cancer is hypermutated or not, using the first image data and the second image data converted by the Z value conversion process and held as training data; and
determining whether the third image data represents an image of hypermutated cancer or not, by inputting the third image data converted by the Z value conversion process into the determination model.
|