| CPC G05B 19/41865 (2013.01) [G05B 13/028 (2013.01); G06Q 50/04 (2013.01); G05B 2219/31352 (2013.01); G05B 2219/32254 (2013.01); G05B 2219/35009 (2013.01)] | 17 Claims |
|
1. A computer-implemented method for dynamically augmenting manufacturing characteristics configured to produce an on-specification product, the method comprising:
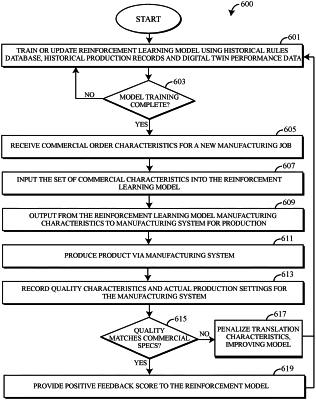
developing, by a processor, a reinforcement learning model using a historical rules database comprising existing rules translating commercial characteristics of a product into the manufacturing characteristics, and historical production settings comprising quality parameters achieved during historical production of on-specification products in accordance with the existing rules;
inputting, by the processor, a set of commercial characteristics to produce the product, wherein the product is steel, and a detected degradation of one or more product manufacturing equipment into the reinforcement learning model;
receiving, by the processor, output from the reinforcement learning model translating the set of commercial characteristics into manufacturing characteristics;
producing the product, by the processor controlling the one or more product manufacturing equipment, with adjustments to the manufacturing characteristics to compensate for the detected degradation of the one or more product manufacturing equipment;
recording, by the processor, quality characteristics of the product produced by one or more manufacturing systems and production settings of the one or more manufacturing systems used to produce the product;
comparing, by the processor, the quality characteristics of the product produced by the one or more manufacturing systems with the commercial characteristics of the product;
rewarding, by the processor, the reinforcement learning model for correctly translating the commercial characteristics to the manufacturing characteristics, whereupon the quality characteristics of the product match the commercial characteristics; and
penalizing, by the processor, the reinforcement learning model for incorrectly translating the commercial characteristics to the manufacturing characteristics, whereupon the quality characteristics of the product do not match the commercial characteristics.
|