| CPC H04W 16/28 (2013.01) [H04W 4/40 (2018.02)] | 38 Claims |
|
1. A synchronization signal block (SSB) receiver, comprising:
a transceiver;
a memory; and
a processor communicatively coupled to the transceiver and the memory,
wherein the transceiver, the memory, and/or the processor are configured to:
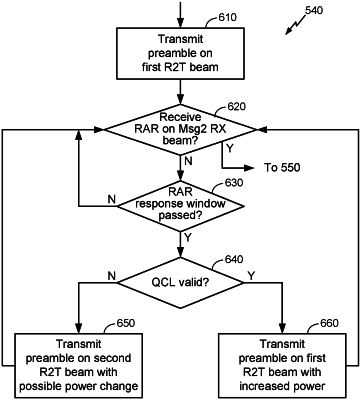
receive, from an SSB transmitter, an SSB on an SSB receive (RX) beam in a transmitter-to-receiver (T2R) direction, the SSB comprising an SSB index corresponding to the SSB RX beam;
transmit, to the SSB transmitter, a physical random access channel (PRACH) preamble on a first receiver-to-transmitter (R2T) beam in a first R2T direction, the PRACH preamble being based on the SSB; and
transmit, to the SSB transmitter, the PRACH preamble on a second R2T beam in a second R2T direction different from the first R2T direction
when a Random Access Response (RAR) is not received from the SSB transmitter within an RAR response window subsequent to transmitting the PRACH preamble on the first R2T beam, and
when a quasi-collocation (QCL) flag is set to QCL invalid,
wherein the QCL flag is set to QCL valid when a QCL assumption is valid and is set to QCL invalid when the QCL assumption is not valid, the QCL assumption being valid when first and second SSB transmissions from the SSB transmitter are QCLed, and is invalid otherwise, the first SSB transmission being a transmission of an SSB beam corresponding to an SSB index k at a first time, and the second SSB transmission being a transmission of an SSB beam corresponding to the same SSB index k at a second time different from the first time.
|