| CPC H04L 41/0895 (2022.05) [H04L 41/0813 (2013.01)] | 17 Claims |
|
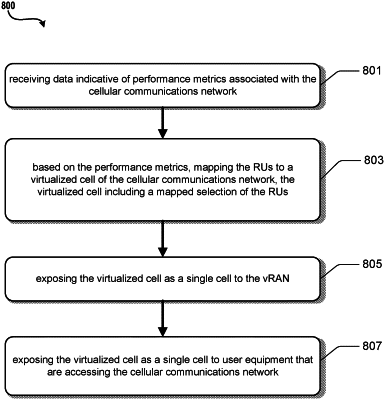
1. A method of dynamically adjusting associations between radio units (RUs) and a virtualized radio access network (vRAN) by a virtual translational layer running in a controller of the vRAN, each of the RUs having a number of antennas and configured to service a cell of a cellular communications network, the method comprising:
exposing, by the virtual translational layer, a virtualized cell as a single cell to the vRAN, wherein the virtualized cell includes a mapped selection of the RUs;
exposing, by the virtual translational layer, the virtualized cell as a single cell to user equipment that are accessing the cellular communications network;
receiving, by the virtual translational layer, data indicative of performance metrics associated with the cellular communications network;
based on the performance metrics, determining variations in signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and network conditions in the cellular communications network;
based on the variations, updating, by the virtual translational layer, the mapping of the RUs to the virtualized cell of the cellular communications network, wherein the updating comprises updating a number of RUs allocated to the virtualized cell based on the variations;
exposing, by the virtual translational layer, the virtualized cell as a single cell to the vRAN, wherein the virtualized cell includes the updated mapping of the RUs; and
exposing, by the virtual translational layer, the virtualized cell as a single cell to user equipment that are accessing the cellular communications network, wherein the virtualized cell includes the updated mapping of the RUs,
thereby enabling the vRAN and the user equipment to interoperate with the virtualized cell as a single cell.
|