| CPC H04B 17/18 (2015.01) [H04B 1/12 (2013.01); H04B 7/0626 (2013.01); H04B 17/12 (2015.01); H04B 17/13 (2015.01); H04L 1/0039 (2013.01); H04L 25/021 (2013.01)] | 14 Claims |
|
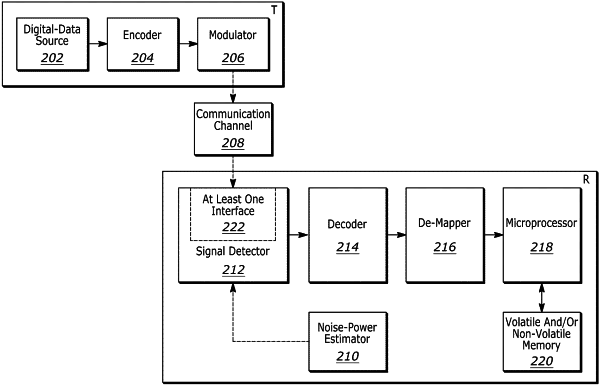
1. A computer-implemented reconstruction method of discrete digital signals in noisy overloaded wireless communication systems that is characterized by a channel matrix of complex coefficients, the method including
Receiving the signal from channel by a signal detector;
Measuring the noise power by a noise power estimator at the receiver;
Forwarding the detected signal and noise power estimation to a decoder that estimates the transmitted symbol-(s),
wherein the estimation of the decoder produces a symbol that could have been transmitted and that is forwarded to a de-mapper, which outputs the bit estimates corresponding to the estimated transmit signal and the corresponding estimated symbol to a microprocessor for further processing; and
wherein the decoder uses the noise power estimation explicitly within the decoding process in such a way that it minimizes the effect of noise amplification.
|