| CPC G09G 3/344 (2013.01) [G09G 3/34 (2013.01); G09G 2320/0257 (2013.01)] | 17 Claims |
|
1. A driving method of an electronic paper display apparatus, wherein the electronic paper display apparatus comprises a controller, a base substrate, a plurality of pixel driving circuits on the base substrate, and an electronic paper film, wherein the electronic paper film comprises a plurality of microstructures, and the plurality of pixel driving circuits comprises a common electrode and a plurality of pixel electrodes among the plurality of microstructures; each of the plurality of microstructures comprises black particles, white particles, and color particles; wherein charges of the black particles have a polarity opposite to a polarity of charges of the white particles and the same as a polarity of charges of the color particles, and a charge-to-mass ratio of the black particles is greater than a charge-to-mass ratio of the color particles; wherein the driving method comprises:
inputting, by the controller, a first driving signal to the pixel electrode of the pixel driving circuit corresponding to a pixel which is required to display black, according to an image to be displayed; and inputting, by the controller, a second driving signal to the pixel electrode of the pixel driving circuit corresponding to a pixel which is required display white, according to the image to be displayed; wherein
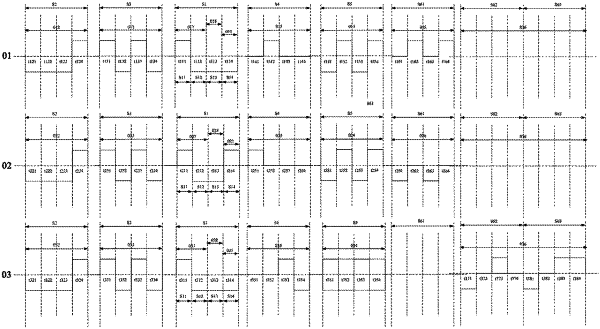
a driving stage of the electronic paper display apparatus comprises a first homogenization stage, and the first homogenization stage comprises a plurality of homogenization sub-stages; at a last one of the plurality of homogenization sub-stages, the first driving signal comprises a first driving sub-signal, and the second driving signal comprises a second driving sub-signal; and
a voltage of the first driving sub-signal has a polarity opposite to the polarity of the black particles; and a voltage of the second driving sub-signal has a polarity opposite to the polarity of the white particles,
wherein the driving method further comprises: inputting, by the controller, a third driving signal to the pixel electrode of the pixel driving circuit corresponding to a pixel which is required to display a color, according to the image to be displayed; wherein at the last one of the plurality of homogenization sub-stages of the first homogenization stage, the third driving signal comprises a third driving sub-signal; and a voltage of the third driving sub-signal has a polarity opposite to the polarity of the color particles,
wherein starting moments of driving of the plurality of homogenization sub-stages of the first homogenization stage sequentially increases, and the plurality of homogenization sub-stages are a first homogenization sub-stage, a second homogenization sub-stage, a third homogenization sub-stage and a fourth homogenization sub-stage; the first driving signal further comprises a nineteenth driving sub-signal at the first homogenization sub-stage and the second homogenization sub-stage; the second driving signal further comprises a twenty-first driving sub-signal at the first homogenization sub-stage and the second homogenization sub-stage; and the third driving signal further comprises a twenty-third driving sub-signal at the first homogenization sub-stage and the second homogenization sub-stage; and
the nineteenth driving sub-signal, the twenty-first driving sub-signal and the twenty-third driving sub-signal each comprise pulse signals with positive and negative voltages sequentially altered.
|