| CPC G06T 7/80 (2017.01) [G01B 11/22 (2013.01); G06T 2207/10028 (2013.01); G06T 2207/10152 (2013.01)] | 11 Claims |
|
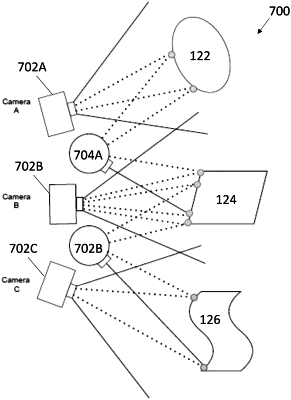
1. A method of calibrating a light source relative to an optical device, the method comprising the steps of:
virtually projecting by a directional light source an image onto a three-dimensional surface of at least one object, the image comprising a virtual grid comprised of predefined points onto an area having the three-dimensional surface of at least one object, each predefined point of the virtual grid corresponding to one of a plurality of termination points of beams cast by the directional light source, at least one of the termination points of the beams are on a surface of the at least one object;
simultaneously capturing, by at least one optical device, data for a plurality of points on the virtual grid by projecting the image into a field of view of the at least one optical device; and
calibrating the directional light source to the at least one optical device to calculate a location and orientation of the optical device using the captured data for the plurality of points, wherein the at least one optical device includes two optical devices, and wherein the step of calibrating the directional light source to the at least one optical device includes calibrating the directional light source to the two optical devices, then calculating a location and orientation of one of the two optical devices to the other of the two optical devices.
|