| CPC G06T 7/0012 (2013.01) [G06T 7/10 (2017.01); G06T 17/20 (2013.01); G16H 30/20 (2018.01); G16H 50/30 (2018.01); G06T 2207/10081 (2013.01); G06T 2207/10116 (2013.01); G06T 2207/30096 (2013.01); G06T 2207/30104 (2013.01); G06T 2210/41 (2013.01)] | 25 Claims |
|
1. A computer-implemented method, comprising:
utilizing one or more computers configured to execute specific program instructions for,
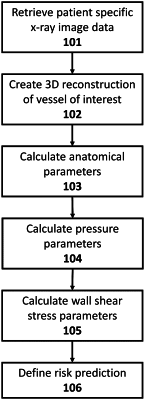
retrieving patient specific image data;
creating a 3D reconstruction of a vessel of interest from the patient specific image data, wherein the vessel of interest represents a subset of a coronary tree that includes a lesion;
determining boundary conditions that include inlet conditions that represent a set of velocity profiles, at a proximal side of the 3D reconstruction, over the multiple moments in time along at least the portion of the cardiac cycle;
calculating at least one of pressure parameters or anatomical parameters based at least in part on a portion of the 3D reconstruction that includes the lesion and the set of velocity profiles;
calculating a wall shear stress (WSS) vectors, based on the 3D reconstruction, at corresponding surface elements for a segment of a surface of the vessel that includes the lesion;
calculating a WSS descriptor based on a divergence of the WSS vectors, the WSS descriptor including a topological shear variation index (TSVI) representing an amount of variation in contraction or expansion applied at surface elements within the segment during at least a portion of a cardiac cycle; and
calculating a myocardial infarction (MI) index based on the WSS descriptor and the at least one of the pressure or anatomical parameters, the MI index representing a likelihood that the lesion will result in an MI.
|