| CPC G06F 30/25 (2020.01) | 19 Claims |
|
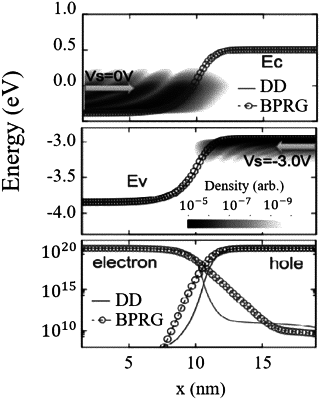
1. A software architecture encoded on a non-transitory computer readable medium, the software architecture processing a physics-based approximation method of modeling interactions between particles, wherein the method comprises:
defining initial conditions for a set of Büttiker probes, wherein each Büttiker probe of the set of Büttiker probes includes various interaction equations between at least one of electrons, holes, photons, and phonons;
initiating a quantum transport method to determine properties of particles interacting with the set of Büttiker probes, wherein the particles include at least one of electrons, holes, photons, and phonons;
quantifying a set of Büttiker probe current input values by calculating a current for each Büttiker probe of the set of Büttiker probes, wherein the current includes at least one of momentum current, particle current, energy current, spin current, and chirality current;
forming a set of continuity equations, using the set of Büttiker probe current input values, such that for each continuity equation a first calculated current of a first Büttiker probe of the set of Büttiker probes is in a particular relation with a second calculated current of a second Büttiker probe of the set of Büttiker probes; and
modeling an interaction between the particles based on the set of continuity equations calculated from the physics-based approximation to improve computational efficiency.
|