| CPC G06F 18/2132 (2023.01) [G06F 18/2415 (2023.01); G10L 21/14 (2013.01); G10L 25/18 (2013.01); G10L 25/30 (2013.01); G10L 25/51 (2013.01)] | 18 Claims |
|
1. A method for detecting fake audios, comprising:
converting audio data into an image representation of the audio data;
providing the image representation of the audio data to a trained machine-learning model, the machine learning model:
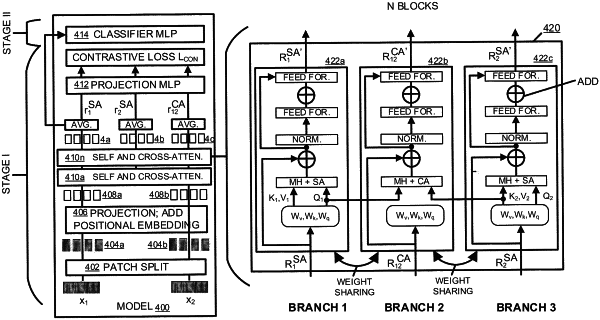
generating, using a trained self-attention branch, one or more representation embeddings corresponding to the image representation of the audio data; and
receiving, using a trained classifier component, the one or more representation embeddings and outputting a classification result; and
wherein the machine-learning model is trained by:
in a first stage, training one or more self- and cross-attention components via contrastive learning,
wherein the one or more self- and cross-attention components comprise a first self-attention branch, a second self-attention branch, and a cross-attention branch, and
wherein the trained self-attention branch is based on the first self-attention branch or the second self-attention branch of the one or more self- and cross-attention components; and
in a second stage, training the classifier component; and
providing the classification result.
|