| CPC G06F 11/1469 (2013.01) [G06F 16/27 (2019.01); G06F 2201/84 (2013.01)] | 33 Claims |
|
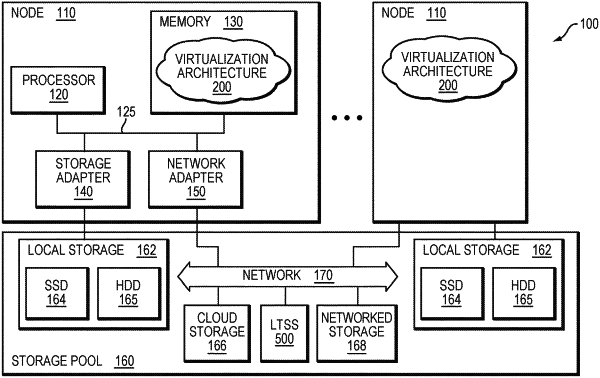
1. A method comprising:
receiving data of a high-frequency snapshot (HFS) of a logical entity from a source data service at an archival storage system according to segments of address ranges of the logical entity as recorded in a persistent log storing the HFS;
constructing a configuration repository associating each segment with a descriptor having a key including a snapshot identifier (ID);
in response to triggering a recovery point,
(i) scanning the configuration repository based on the snapshot ID to collect descriptors associated with the snapshot ID; and
(ii) constructing a searchable index data structure based on the collected descriptors to represent the recovery point, wherein the searchable index data structure maps each segment address range to an object in the archival storage system, and wherein the searchable index data structure is used to hydrate the recovery point at a target data service.
|