| CPC G01N 33/6848 (2013.01) [G01N 30/02 (2013.01); G01N 33/5375 (2013.01); G01N 33/6857 (2013.01); G01N 2030/027 (2013.01)] | 4 Claims |
|
1. A detection method for a monoclonal antibody in a sample, comprising:
(a) capturing monoclonal antibodies in a sample to immobilize the monoclonal antibodies in pores of a porous body, wherein the porous body has Protein A, which functions as a linker molecule to site-specifically interactive with the monoclonal antibody, immobilized in the pores;
(b) bringing the porous body in which the monoclonal antibodies are immobilized into contact with nanoparticles on which protease is immobilized to conduct selective protease digestion of the monoclonal antibodies, wherein the protease is trypsin; and
(c) detecting, by a liquid chromatography mass spectrometry (LC-MS), peptide fragments obtained by the selective protease digestion;
wherein the method further comprises, after the step (a):
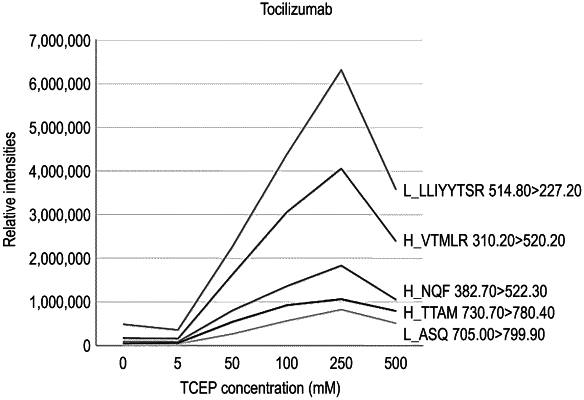
(a′) adding a reducing agent and conducting a reduction reaction under a strong acidic condition of a pH of 2.5 or lower; and
(a″) removing the reducing agent after conducting the reduction reaction and before conducting the selective protease digestion,
wherein the reducing agent is Tris(2-carboxyethyl) phosphine (TCEP), or a hydrochloride salt thereof in a range of 100 to 500 mM.
|