| CPC G01N 27/414 (2013.01) [A61M 37/0015 (2013.01); G01N 27/4145 (2013.01); G01N 27/4146 (2013.01); G01N 33/5438 (2013.01)] | 25 Claims |
|
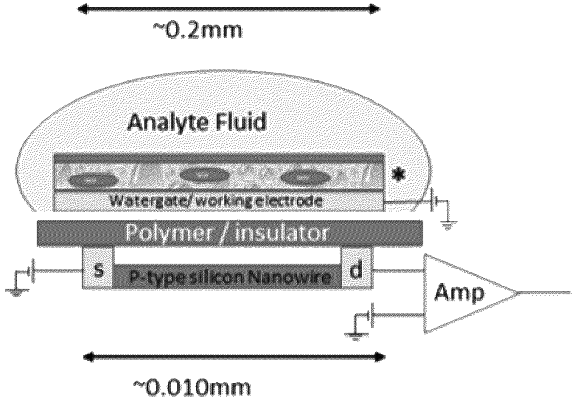
1. A microprobe sensing device, comprising:
a plurality of microprobes, each microprobe including a tip configured to be inserted into an analyte solution and a sensor positioned at the tip, wherein each sensor comprises:
a working electrode configured to be positioned in contact with the analyte solution,
a voltage source coupled to the working electrode,
an amplifier comprising:
a source terminal,
a drain terminal, and
a plurality of nanowires,
wherein each of the plurality of nanowires electrically connects the source terminal to the drain terminal,
wherein each of the plurality of nanowires has a major cross section dimension in the range of 1 to 500 nanometers,
a back gate electrode,
a dielectric layer positioned between the back gate electrode and the amplifier, and
an insulator having a first side and a second side opposite the first side,
wherein the working electrode is positioned to the first side of the insulator, and
wherein (a) the source terminal, (b) the drain terminal, and (c) the plurality of nanowires are positioned to the second side of the insulator,
whereby the insulator is configured to prevent direct electrical contact between the working electrode and either (a) the source terminal, (b) the drain terminal, or (c) the plurality of nanowires, and
whereby the insulator is configured to prevent direct contact between the analyte solution and either (a) the source terminal, (b) the drain terminal, or (c) the plurality of nanowires,
wherein the sensor is configured such that only the working electrode contacts the analyte solution, which is through an exposed part,
wherein the working electrode is configured such that, when a chemical species is present in the analyte solution, a variation in an electrical field at a location of the plurality of nanowires is induced, and
wherein the plurality of nanowires is configured such that, when the electrical field varies, a corresponding variation in an electrical current between the source terminal and the drain terminal is induced.
|