| CPC F16H 61/04 (2013.01) [B60W 20/30 (2013.01); F16H 59/18 (2013.01); F16H 59/42 (2013.01); F16H 59/66 (2013.01); F16H 63/502 (2013.01); F16H 2061/0474 (2013.01)] | 7 Claims |
|
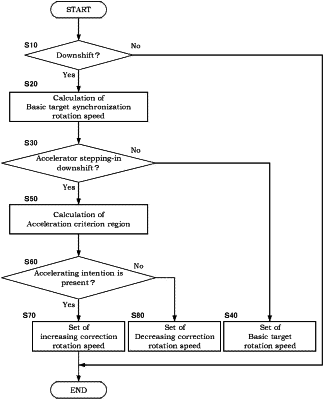
1. A shift control method implemented in a vehicle equipped with an automatic transmission for controlling an input shaft rotation speed of the automatic transmission to a target input shaft rotation speed during a shift, comprising:
setting a basic target synchronization rotation speed that is a basic target value of the input shaft rotation speed during the shift;
determining whether or not the shift is a downshift with a driving force requirement to the vehicle where an accelerator opening of the vehicle is greater than zero;
in response to determining that the shift is the downshift with the driving force requirement, determining whether or not an accelerating intention is present by comparing the accelerator opening with an accelerating intention criterion region;
in response to determining that the accelerator opening is more than the accelerating intention criterion region, setting a first target input shaft rotation speed as the target input shaft rotation speed, the first target input shaft rotation speed being obtained by increasing the basic target synchronization rotation speed; and
in response to determining that the accelerator opening is greater than zero and equal to or below the accelerating intention criterion region, setting a second target input shaft rotation speed as the target input shaft rotation speed, the second target input shaft rotation speed being obtained by maintaining or decreasing the basic target synchronization rotation speed.
|