| CPC C12P 7/16 (2013.01) [C01B 33/12 (2013.01); C01C 1/086 (2013.01); C08G 61/124 (2013.01); E21B 43/241 (2013.01); B82Y 40/00 (2013.01); C01P 2004/64 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
1. A method for reducing condensate in a subsurface formation, the method comprising:
introducing a reactive mixture comprising an aqueous solution, urea, dopamine, a silica nanoparticle precursor, a silane grafting compound, and an alcohol compound into the subsurface formation;
generating ammonia through thermal decomposition of the urea;
hydrolyzing the silica nanoparticle precursor, thereby forming silica nanoparticles;
grafting the silane grafting compound onto the silica nanoparticles, thereby forming functionalized silica nanoparticles;
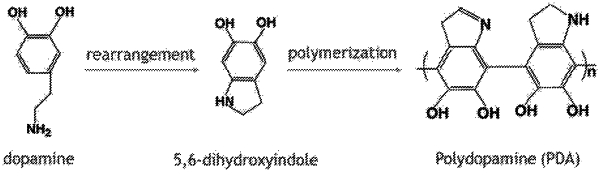
polymerizing the dopamine, thereby forming polydopamine; and
attaching the functionalized silica nanoparticles to the subsurface formation via the polydopamine, thereby reducing condensate in the subsurface formation.
|