| CPC C12P 17/08 (2013.01) [C12P 7/42 (2013.01); C12P 7/44 (2013.01); C12P 17/04 (2013.01)] | 16 Claims |
|
1. A chemo-enzymatic process for producing Z-9 cyclohexadecenolide having the chemical structure:
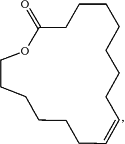 the process comprising:
(i) culturing a recombinant microorganism in the presence of a carbon-based feedstock, wherein
the recombinant microorganism is a bacterium, cyanobacterium, yeast, or filamentous fungus,
the recombinant microorganism is genetically engineered to overexpress or to exogenously express an ω-hydroxylase or oxygenase of E.C. 1.14.15.3 compared to a native host cell, and
the recombinant microorganism produces an unsaturated ω-hydroxy fatty acid derivative that is ω-hydroxy-cis-9-hexadecenoic acid having the chemical structure:
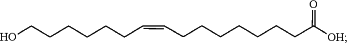 and
(ii) contacting the ω-hydroxy-cis-9-hexadecenoic acid ex vivo with a reagent under conditions sufficient to produce the Z-9 cyclohexadecenolide, wherein the contacting comprises dehydration, lactonization, or a combination thereof.
|