| CPC C07D 519/00 (2013.01) [C07D 471/04 (2013.01); C07D 491/20 (2013.01)] | 25 Claims |
|
1. A compound of Formula (I):
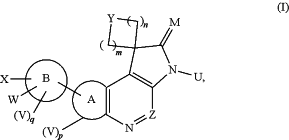 or a stereoisomer, enantiomer, tautomer thereof or a mixture thereof;
or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof;
wherein
m is 0, 1, 2, 3, or 4;
n is 1, 2, 3, or 4;
p and q are each independently 0, 1, 2, or 3;
 is a fused cyclyl, a fused heterocyclyl, a fused aryl or a fused heteroaryl;
 is a mono-cyclic or bi-cyclic ring, a mono-heterocyclic or bi-heterocyclic ring, an aryl or heteroaryl;
Y is —(C(R1a)H—, —C(O)—, —O—, —N(R5)—, —S(O)r— (where r is 0, 1 or 2), —S(O)t(NR5)— (where t is 1 or 2), —P(O)(R3)—O—, —O—P(O)(R3)—, P(O)(R3)—N(R5)—, —N(R5)—P(O)(R3)—, —CHF—, —CF2—, —OC(O)—, —C(O)O—, —C(O)N(R5)— or —N(R5)C(O)—,
M is O, S, or NR5;
U is hydrogen or alkyl;
V, W, and X are each independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted alkyl, optionally substituted alkenyl, optionally substituted alkynyl, halo, optionally substituted haloalkyl, optionally substituted haloalkenyl, optionally substituted haloalkoxy, optionally substituted cycloalkyl, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heterocyclyl, optionally substituted heteroaryl, —R6—CN, —R6—NO2, —R6—OR5, —R6—N(R4)R5, —O—R6—N(R4)R5, —N═C(R4)R5, —S(O)rR4, —OS(O)2CF3, —R6—C(O)R4, —C(S)R4, —R6—C(O)OR4, —C(S)OR4, —R6—C(O)N(R4)R5, —C(S)N(R4)R5, —N(R5)C(O)R4, —N(R5)C(S)R4, —N(R5)C(O)OR4, —N(R5)C(S)OR4, —N(R5)C(O)N(R4)R5, —N(R5)C(S)N(R4)R5, —N(R5)S(O)tR4, —N(R5)S(O)tN(R4)R5, —R6—S(O)tN(R4)R5, —O—P(O)(R4)R5, —O—P(O)R4O(R4), —O—P(O)R4N(R4)R5, —N(R5)—P(O)(R4)R5, —N(R5)—P(O)R4O(R4), —N(R5)—P(O)R4N(R4)R5, —N(R5)—P(O)O(R4)N(R4)R5, —N(R5)—P(O)N(R4)R5N(R4)R5, —N(R5)C(═NR5)R4, —N(R5)C(═NR5)N(R4)R5, and —N(R5)C(═N—CN)N(R4)R5, wherein each r is independently 0, 1, or 2 and each t is independently 1 or 2;
or two adjacent V, or W, or X together with the carbon ring atoms to which they are directly attached, form a fused ring selected from optionally substituted cycloalkyl, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heterocyclyl, and optionally substituted heteroaryl;
Z is C(R1a) or N;
R1a is a hydrogen, optionally substituted alkyl, halo, CN, NO2, or —OR5;
R3 is an optionally substituted alkyl, —OR5, or —N(R4)R5;
each R4 and R5 is independently selected from group consisting of hydrogen, optionally substituted alkyl, optionally substituted alkenyl, optionally substituted alkynyl, optionally substituted haloalkyl, optionally substituted alkoxyalkyl, optionally substituted cycloalkyl, optionally substituted aryl, optionally substituted heterocyclyl, and optionally substituted heteroaryl;
or when R4 and R5 are each attached to the same nitrogen atom, R4 and R5, together with the nitrogen atom to which they are attached, form a optionally substituted heterocyclyl or optionally substituted heteroaryl; and
each R6 is a direct bond or a linear or branched optionally substituted alkylene chain, a linear or branched optionally substituted alkenylene chain, a linear or branched optionally substituted alkynylene chain, or optionally substituted heterocyclylene.
|