| CPC B61G 11/12 (2013.01) | 8 Claims |
|
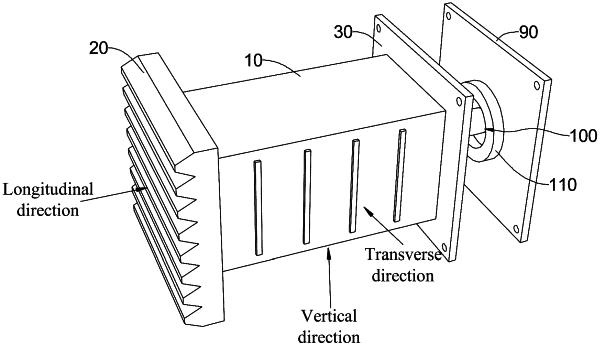
1. A guide-type anti-climbing energy-absorbing device based on hydraulic shearing, comprising:
an energy-absorbing tube;
an anti-climbing portion;
a first connecting portion;
a plurality of partition plates; and
two guide plates;
wherein the anti-climbing portion is arranged at a first end of the energy-absorbing tube, and the first connecting portion is arranged at a second end of the energy-absorbing tube;
the plurality of partition plates are sequentially arranged inside the energy-absorbing tube along an axial direction of the energy-absorbing tube and are configured to divide an interior of the energy-absorbing tube into a plurality of first energy-absorbing cavities; and the plurality of first energy-absorbing cavities are each filled with a first honeycomb body;
the two guide plates are symmetrically arranged in the energy-absorbing tube along a vertical direction of the energy-absorbing tube; and
each of the two guide plates is arranged obliquely and has a connecting end and a free end opposite to each other; the connecting end is connected to the anti-climbing portion; the free end passes through the plurality of partition plates in sequence to extend outside the first connecting portion; each of the two guide plates is in slidable fit with the first connecting portion; and the connecting end is closer to an axis of the energy-absorbing tube relative to the free end; and
wherein first honeycomb bodies filled in the plurality of energy-absorbing cavities are arranged in an ascending order in terms of yield strength along a direction from the anti-climbing portion to the first connecting portion.
|