| CPC A61N 1/36039 (2017.08) [H04R 25/606 (2013.01); H04R 2225/67 (2013.01)] | 36 Claims |
|
1. A method, comprising:
determining an electrical stimulation boundary within a cochlea of a recipient of an auditory prosthesis comprising an intra-cochlear stimulating assembly, the recipient having residual hearing at an apical side of the electrical stimulation boundary, wherein the intra-cochlear stimulating assembly comprises a plurality of longitudinally spaced electrodes forming a plurality of multipolar stimulation channels; and
determining current weights for at least one of the plurality of multipolar stimulation channels at a basal side of the electrical stimulation boundary,
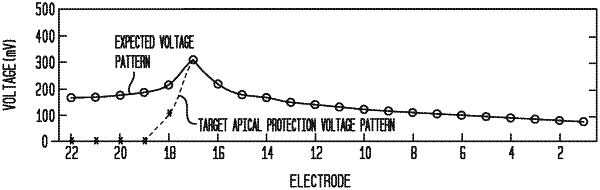
wherein the current weights for the at least one of the plurality of multipolar stimulation channels at the basal side of the electrical stimulation boundary are set for delivery of current signals to the cochlea via the at least one of the plurality of multipolar stimulation channels to evoke perception of one or more frequencies of a sound obtained at the auditory prosthesis while creating nulled voltage fields across the apical side of the electrical stimulation boundary and to create voltages at the plurality of longitudinally spaced electrodes that include a peak voltage and that asymmetrically decrease from the peak voltage.
|