| CPC A61K 31/575 (2013.01) [A61K 9/0014 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
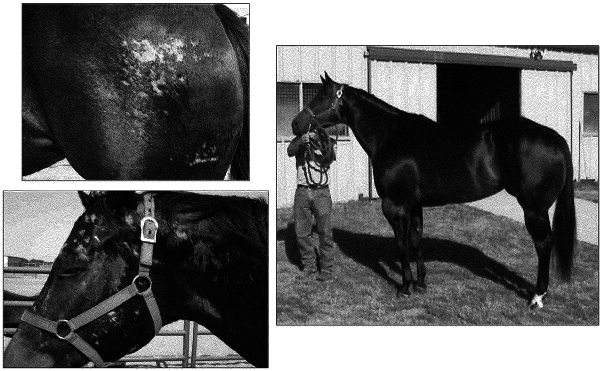
1. A method of regenerating tissue and/or preventing tissue atrophy, the method comprising:
providing a treatment composition including one or more cationic steroidal antimicrobial (CSA) compounds in a carrier;
directly applying the treatment composition to targeted tissue of a subject that is in need of regeneration and is not infected with a microbial infection or associated with a dermal tissue wound; and
the one or more CSA compounds stimulating tissue-specific stem cells to proliferate and promote tissue regeneration and/or prevent tissue atrophy at the targeted tissue to which it is applied, wherein the tissue-specific stem cells are selected from the group consisting of follicular stem cells, hematopoietic stem cells, neural stem cells, and stem cells found in one or more of peripheral blood, brain, spinal cord, dental pulp, blood vessels, skeletal muscle, hair follicle tissue, epithelia of the digestive system, cornea, retina, liver, or pancreas; wherein the targeted tissue is tissue damaged as a result of stroke, an autoimmune disease, a brain injury, or a cardiac injury or disorder.
|