| CPC G01N 21/4738 (2013.01) [G01J 3/26 (2013.01); G01N 21/65 (2013.01); G01N 2021/8867 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
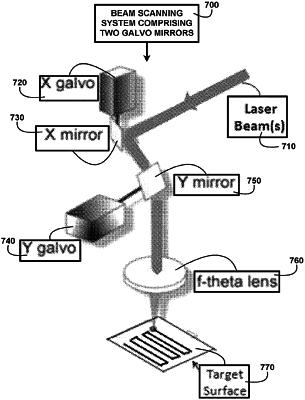
|
1. A method for in-situ inspection of an object, comprising:
providing a pulsed laser source during the in-situ inspection of a surface of the object for modifying at least one of an optical, mechanical, or chemical property of a first region of the surface;
directing a process laser source through an optics path to shape, position and focus a pulsed laser beam at the first region;
directing a probe illumination light beam to the optics path to produce a combined and collinear optical light path of the probe illumination light beam and the pulsed laser beam to focus and deliver the combined and collinear optical light path at a same region on the surface;
substantially superimposing a first focus spot of the probe illumination light beam over a second focus spot of the pulsed laser beam on an illuminated region of the surface;
collecting back-scattered probe light reflected off the illuminated region and directing the collected light from the illuminated region through at least a portion the combined and collinear optical light path to provide a bi-directional common optic path for the pulsed laser beam, probe illumination light beam, and the collected back-scattered probe light from the illuminated region;
continually assessing modifications to each target region and controlling predetermined modifications to the next region by automatically adjusting laser pulse intensities of the laser beam; and
constructing an image of the surface with at least one pixel and at least one pixel value, wherein each pixel represents a region on the surface and each pixel value represents a value of collected probe light at a region of a defined position, wherein the constructed image is used to adjust the laser pulse intensities for predetermined modifications to other regions.
|