| CPC H04L 65/403 (2013.01) [G06F 8/30 (2013.01); G06F 40/30 (2020.01); G06N 20/00 (2019.01); H04L 51/02 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
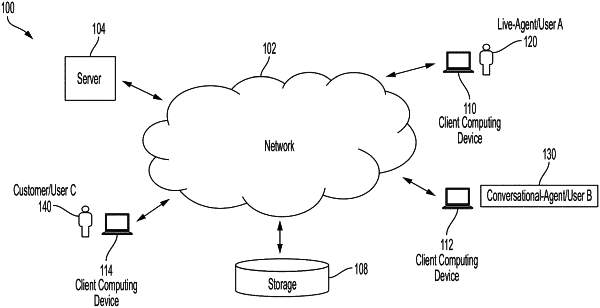
1. A computer-implemented method of responding to an inquiry received electronically at a synchronous conferencing system (SCS), the computer-implemented method comprising:
passing messages from a user into an SCS during an SCS session;
based at least in part on a recognition that the messages include a first type of user inquiry comprising a first user inquiry complexity level that can be understood and processed using a first alternative operation mode operable to occur between the user and a first agent, switching the SCS session to the first alternate operation mode comprising:
using a processor of the SCS to generate a script comprising one or more script computer instructions operable to perform cognitive determinations have a first complexity level that can analyze the first type of user inquiry comprising the first user inquiry complexity level;
using the processor to execute the script computer instructions to generate script computer instruction results, wherein the script computer instruction results comprise inquiry response information that is responsive to the first type of user inquiry; and
based at least in part on the first type of user inquiry and the inquiry response information, using the processor to generate an inquiry response from the second agent that is responsive to the first type of user inquiry.
|