| CPC G16H 50/50 (2018.01) | 20 Claims |
|
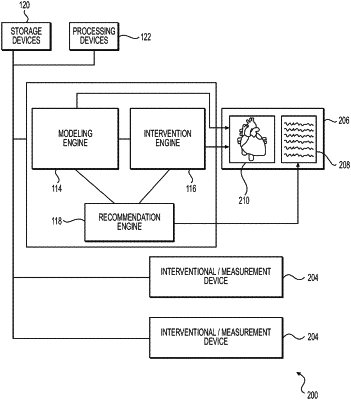
1. A computer-implemented method of automatically updating a cardiovascular model, comprising:
receiving, via at least one processor, a patient-specific anatomical model of at least one cardiovascular vessel and at least one characteristic associated with the patient-specific anatomical model;
using the at least one processor to transmit a representation of at least one of the patient-specific anatomical model or the at least one associated characteristic to a display unit;
receiving, at the at least one processor, additional patient-specific data relating to the patient-specific anatomical model from a medical procedure;
determining, using the at least one processor, a correspondence between the additional patient-specific data and at least one of the patient-specific anatomical model or the at least one associated characteristic by determining a location of the patient-specific anatomical model to which the additional patient-specific data applies;
identifying, using the at least one processor, a discrepancy between the additional patient-specific data and at least one of the patient-specific anatomical model or the at least one associated characteristic, the discrepancy corresponding to a mismatch between at least one point of the additional patient-specific data and a corresponding aspect of at least one of the patient-specific anatomical model or the at least one associated characteristic;
modifying, using the at least one processor, at least one of the patient-specific anatomical model or the at least one associated characteristic to reduce or eliminate the discrepancy; and
transmitting, using the at least one processor, an updated representation of at least one of the patient-specific anatomical model or the at least one associated characteristic to the display unit.
|