| CPC G16H 20/00 (2018.01) [G06N 20/00 (2019.01); G16H 50/30 (2018.01); G16H 50/70 (2018.01)] | 19 Claims |
|
1. A system, comprising:
a memory that stores computer executable components;
a processor that executes the computer executable components stored in the memory, wherein the computer executable components comprise:
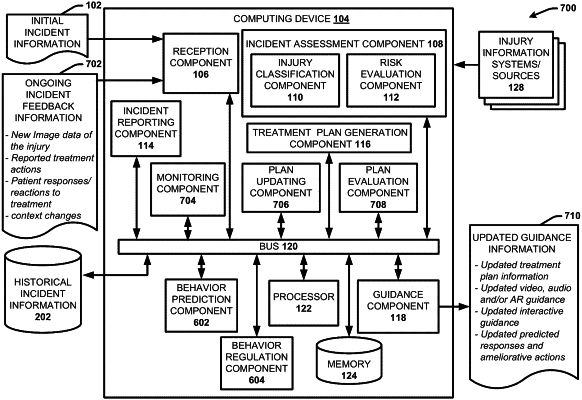
an incident reporting component that activates one or more sensors that gathers audio information and video data for a patient that has endured an injury and causes an incident report for the injury endured by the patient to be initiated based on collection of the audio information and the video data by the one or more sensors and electronically attaching to the system, via a computer network between a device having the one or more sensors and the system, the audio information to the system;
an injury classification component that classifies a type of the injury endured by the patient;
a risk evaluation component that employs one or more machine learning models to estimate a risk level associated with the injury, based on the type of the injury and on context information regarding the patient;
an affinity component that determines one or more affinities of the patient related to a treatment plan for the injury, the one or more affinities being based on one or more monitored behavioral reactions of the patient to the treatment plan that occur during treatment of the patient, wherein the one or more behavioral reactions comprises monitored body movements of the patient, wherein the one or more machine learning models comprise a time information fusion-based approach for the video data, wherein the video data is considered a plurality of fixed-sized segments and the one or more machine learning models extend connectivity of a network in time dimension to learn spatio-temporal features for classification based on a plurality of connectivity patterns comprising early fusion, slow fusion or late fusion.
|