| CPC G06F 8/70 (2013.01) [G06F 8/36 (2013.01)] | 18 Claims |
|
1. A system for automatically scoring open-source libraries on a state of reuse in a software project, the system comprising:
one or more processors and memory storing instructions that, when executed by the one or more processors, cause the one or more processors to perform operations comprising:
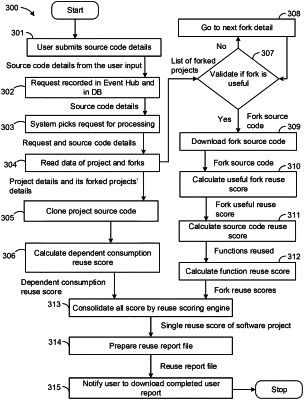
extracting information about the software project from a source code repository;
determining whether the extracted information includes information regarding any forked projects;
calculating, upon determining that a forked project is included, a useful fork reuse score for the forked project based on source code attributes including a source code class;
creating a tree structure for the source code class;
identifying functions from the tree structure of the source code class;
identifying similar code sections from the two source code files;
calculating a code attributes reuse score based on the similar code sections;
calculating a dependent consumption reuse score which indicates how much a function is reused by a dependent class; and
calculating a unified reuse score based on the useful fork reuse score of the forked project and the dependent consumption reuse score for the analyzed project;
wherein calculating the useful fork reuse score comprises:
collecting data of commit history records associated with source code of forked open-source projects;
retrieving each commit history record with the date and timestamp, and the number of files affected by each commit in the commit history record;
determining a number of commits performed during a defined interval to generate a source code commit activity score, wherein whether the fork is active or not is dependent on the source code commit activity score;
selecting useful forks by verifying whether regular commits are happening to a forked repository and ignoring other forks based on one of: no activity and activity being less than a threshold limit;
validating the forked project for its usefulness based on commit history trends of the forked project and a parent project;
comparing respective source code commit history rates of the parent project and the forked project to generate a weighted score based on increased or decreased rate of the commits;
combining the respective source code commit history rates of the parent project and the forked project to generate a final score for the forked projects by further comparing their scores against a set threshold baseline score; and
determining, via the scores, the useful fork reuse score of the forked project.
|