| CPC G02B 21/008 (2013.01) [G01N 21/6428 (2013.01); G01N 21/84 (2013.01); G02B 21/0036 (2013.01); G02B 21/0076 (2013.01)] | 10 Claims |
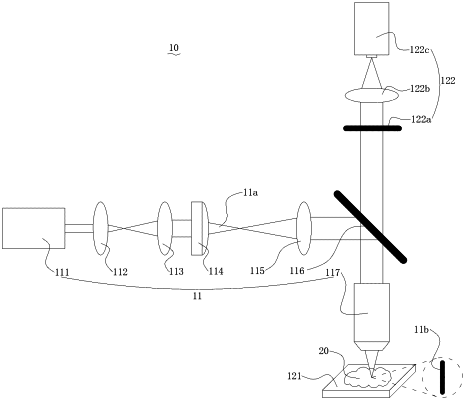
|
1. A high-throughput optical sectioning imaging method, comprising the following steps:
at S1, modulating a light beam into a modulated light beam capable of being focused on a focal plane of an objective lens and being defocused on a defocusing plane of the objective lens, the modulated light beam having incompletely identical modulated intensities on the focal plane of the objective lens;
at S2, imaging, by a camera, in different rows of pixels, a same sample under illumination of the modulated light beam to form sample images, a formula expression of the formed sample image being:
I(i)=Iinf(i)+Iout,
where I(i) is a sample image formed in an ith row of pixels, f(i) is a modulation intensity corresponding to the sample image I(i), Iin is a focal plane image of the sample image, and Iout is a defocusing plane image of the sample image;
at S3, obtaining focal plane images of the sample images in the different rows of pixels by demodulating the sample images according to a demodulation algorithm, the focal plane image being an optical sectioning image, and a demodulation formula of the demodulation algorithm being Iin=c×|βI1−αI2|,
where α and β are positive integers, c is a constant greater than 0, I1 is an accumulated sum of sample images acquired in a pixels, and I2 is an accumulated sum of sample images acquired in β pixels; an accumulated value of modulation intensities corresponding to the sample images in the α pixels is different from an accumulated value of modulation intensities corresponding to the sample images in the β pixels.
|