| CPC G01C 21/005 (2013.01) [G01C 21/20 (2013.01)] | 14 Claims |
|
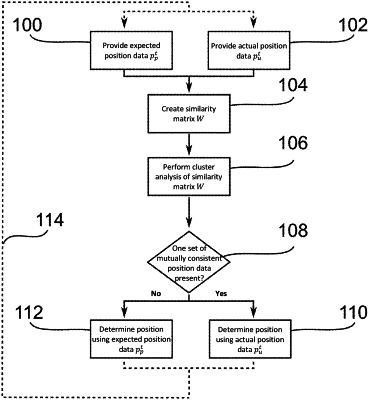
1. A method for determining a position of a robot, the method comprising:
providing expected position data including expected positions of the robot over time, using a first sensor device;
providing actual position data including actual positions of the robot over time, using a second sensor device;
determining, with a computer, mutually consistent expected position data and actual position data by (i) creating a similarity matrix between the expected position data and the actual position data and (ii) analyzing the similarity matrix by way of cluster analysis;
detecting, with the computer, outliers in the expected position data and the actual position data based on the similarity matrix;
determining, with the computer, position data that are free from outliers depending on the mutually consistent expected position data and actual position data, the detected outliers being omitted from the position data that are free from outliers, the actual position data being determined as the position data that are free from outliers in response to at least one of (i) the mutually consistent expected position data and actual position data including precisely one set of mutually consistent expected position data and actual position data and (ii) the mutually consistent expected position data and actual position data including a most recent in time actual position of the robot;
determining, with the computer, the position of the robot based on the position data that are free from outliers; and
autonomously navigating, with a controller, the robot to perform a task using the determined position of the robot.
|