| CPC C12Q 1/6869 (2013.01) [G06N 3/088 (2013.01); G16B 30/20 (2019.02); G16B 40/10 (2019.02); G16B 40/30 (2019.02)] | 20 Claims |
|
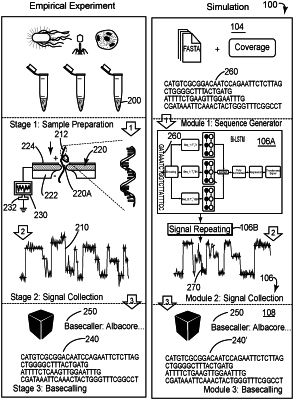
1. A method for simulating reads for a sequencing technology of biopolymers that uses nanopores, the method comprising:
generating, with a sequence generator module, an input nucleotide sequence having plural k-mers, wherein the input nucleotide sequence satisfies coverage and length distribution associated with the sequencing technology that uses the nanopores;
simulating with a deep learning simulator, actual electrical current signals corresponding to the input nucleotide sequence;
identifying reads that correspond to the actual electrical current signals; and
displaying the reads,
wherein the deep learning simulator includes a context-dependent deep learning model that takes into consideration a position of a k-mer of the plural k-mers on the input nucleotide sequence when calculating a corresponding actual electrical current.
|