| CPC B64C 27/26 (2013.01) [B64C 3/385 (2013.01); B64C 9/10 (2013.01); B64C 9/30 (2013.01); B64C 13/16 (2013.01); B64C 13/48 (2013.01); B64C 2211/00 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
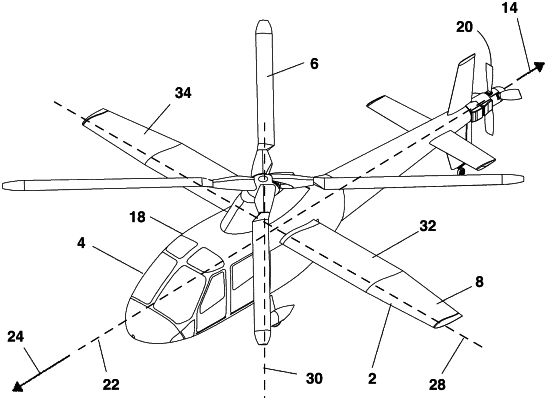
1. A rotary-wing aircraft, the rotary-wing aircraft comprising:
a. a fuselage, the fuselage having an aircraft longitudinal axis defining a forward direction;
b. a rotor attached to the fuselage, the rotor having a rotor axis of rotation generally normal to the longitudinal axis, the rotor being configured to rotate about the rotor axis of rotation to provide lift to the rotary-wing aircraft;
c. a supplemental wing attached to the fuselage, the supplemental wing being rotatable about a pitch axis with respect to the fuselage, the supplemental wing defining a span, the pitch axis being substantially parallel to the span, the pitch axis being substantially normal to the longitudinal axis and substantially normal to the rotor axis of rotation, the supplemental wing defining a chord substantially normal to the span, the supplemental wing being rotatable about the pitch axis between a forward flight position and a hover position, the chord being substantially parallel to the longitudinal axis when the supplemental wing is in the forward flight position, the chord being substantially normal to the longitudinal axis when the supplemental wing is in the hover position, the supplemental wing being rotatable through a plurality of positions intermediate to the hover and forward flight positions;
d. the supplemental wing defining a leading edge and a trailing edge, the supplemental wing defining a aerodynamic center and an angle of attack when a relative wind is moving over the supplemental wing from the leading edge to the trailing edge, the aerodynamic center being aft of the pitch axis when the aircraft is flying in the forward direction in the forward flight position so that a lift acting through the aerodynamic center applies a negative pitching moment to the supplemental wing when the aircraft is flying in the forward direction with the supplemental wing in the forward flight position;
e. wherein the supplemental wing has an aerodynamic configuration to apply an positive pitching moment to the supplemental wing when the aircraft is flying in the forward direction with the supplemental wing in the forward flight position so that the supplemental wing rotates about the pitch axis to an equilibrium position in which the positive pitching moment balances the negative pitching moment;
f. wherein the rotor has a control authority over the rotary wing aircraft in flight, the aircraft further comprising: a trim control system, the trim control system including an airspeed sensor to detect a speed of the relative wind over the supplemental wing from the leading edge to the trailing edge when the aircraft is flying in the forward direction and the supplemental wing is in the forward flight position, the trim control system including a movable trim control surface at the trailing edge of the supplemental wing, the trim control system having a configuration to depress the trim control surface when the aircraft is flying in the forward direction at greater than a predetermined speed so that the trim control surface increases the negative pitching moment of the supplemental wing and reduces the amount of lift generated by the supplemental wing, whereby the control authority of the rotor is preserved.
|