| CPC A61B 5/0205 (2013.01) [A61B 5/0004 (2013.01); A61B 5/6898 (2013.01); A61B 5/725 (2013.01); A61B 5/7225 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
1. A device for performing remote physiological signal monitoring on a subject, wherein the device comprises:
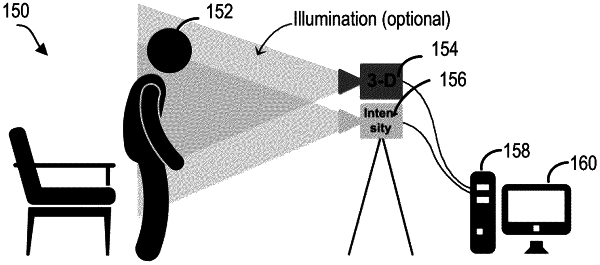
a first camera unit having a first pair of collocated cameras having a same field of view, the first pair of collocated cameras comprising a depth camera with a depth channel for providing depth data and an intensity camera with an intensity channel for providing intensity data obtained from capturing depth images and intensity images, respectively, of the subject;
a memory for storing program instructions for performing a method of remote physiological signal monitoring on the subject; and
a processor unit that includes at least one processor that is operably coupled to the first camera unit for receiving the depth data and the intensity data and operatively coupled to the memory for executing the program instructions for performing the method of physiological signal monitoring which configures the at least one processor to:
detect at least one region of interest (ROI) for images in the intensity data and/or the depth data;
generate waveforms for the intensity data and the depth data where a given data point in the waveforms is obtained using pixel values in the at least one ROI for the images in the intensity data and the depth data;
estimate at least one heart rate (HR) value for the subject by performing high frequency bandpass filtering on the waveforms of the intensity data and the depth data to obtain corresponding HR waveforms for the intensity data and the depth data; performing peak detection on the HR waveforms to determine a series of peaks and estimating the at least one HR value based on temporal spacing between the series of peaks in the HR rate waveforms; and
estimate at least one respiratory rate (RR) value for the subject by performing low frequency bandpass filtering on the waveforms of the intensity data and the depth data to obtain corresponding respiratory waveforms for the intensity data and the depth data; performing peak detection on the respiratory waveforms to determine a series of peaks and estimating the at least one RR value based on temporal spacing between the series of peaks in the respiratory waveforms.
|