| CPC H01L 21/6833 (2013.01) [H01J 37/32724 (2013.01); H01L 21/68757 (2013.01)] | 18 Claims |
|
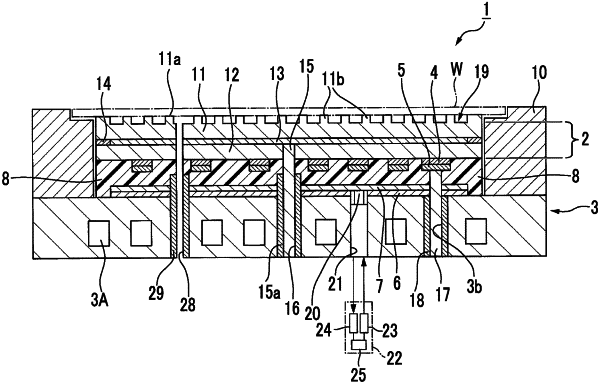
1. An electrostatic chuck device comprising:
a base having one main surface serving as a mounting surface on which a plate-shaped sample is mounted; and
an electrode for electrostatic attraction provided on a side opposite to the mounting surface in the base or in an interior of the base,
wherein the electrode for electrostatic attraction is made of a composite sintered body that includes a matrix phase having insulation properties and a dispersed phase having a lower volume resistivity value than the matrix phase, and
wherein the dispersed phase of the composite sintered body comprises a plurality of aggregated portions comprising metal, silicon, and carbon, the aggregated portions each having a Maximum Feret Diameter of 30 μm or more, the Maximum Feret Diameter being the maximum value of the interval between two parallel lines when a measurement region of each aggregated portion is sandwiched between the two parallel lines.
|