| CPC C09K 8/594 (2013.01) [C09K 2208/10 (2013.01)] | 11 Claims |
|
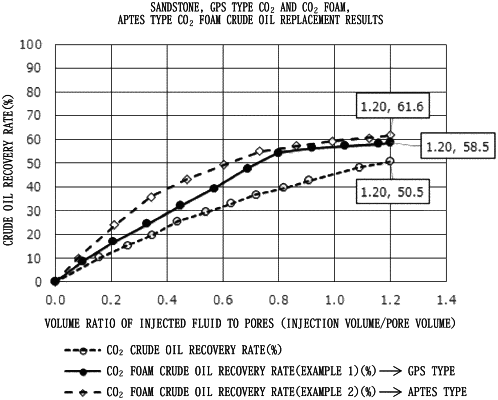
1. A crude oil recovery method for recovering crude oil from a subsurface hydrocarbon-containing reservoir, the method comprising:
step (a): injecting an aqueous sol, water and carbon dioxide, each alternatingly or simultaneously, into a subsurface oil reservoir;
wherein the aqueous sol comprises silica particles having an average particle diameter of 1 to 100 nm as measured by dynamic light scattering and having surfaces at least partially coated with a silane compound having a hydrolyzable group, wherein the hydrolyzable group is selected from the group consisting of an alkoxy group, an acyloxy group, and a halogen group, the silica particles serving as a dispersoid and being dispersed in an aqueous solvent having a pH of 1.0 or more to 6.0 or less serving as a dispersion medium; and
step (b): following the injecting, recovering oil extracted by an oil production well drilled into the subsurface oil reservoir.
|