| CPC A61B 5/746 (2013.01) [A61B 5/02055 (2013.01); A61B 5/0261 (2013.01); A61B 5/14539 (2013.01); A61B 5/14546 (2013.01); A61B 5/14551 (2013.01); A61B 5/6852 (2013.01); A61B 5/7275 (2013.01); A61B 5/0215 (2013.01); A61B 5/02416 (2013.01); A61B 5/0816 (2013.01); A61B 2560/0228 (2013.01)] | 19 Claims |
|
1. A method comprising the steps of:
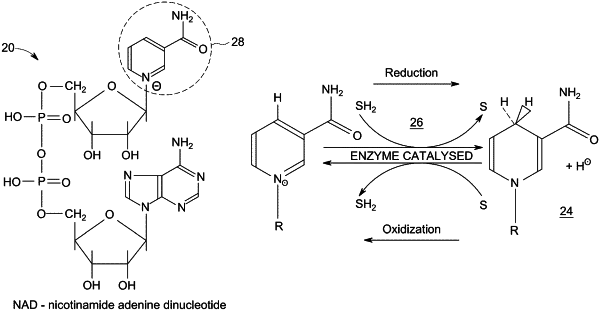
emplacing in an organ of interest in a patient, a set of sensors designed to monitor parameters of the organ of interest, including at least nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADHI) level and at least one parameter from among the group consisting of tissue blood flow (BFI), blood hemoglobin (HbO2I), and tissue reflectance (TRI), and substantially continuously, computing a vitality index of the organ of interest based at least in part on the parameters monitored by the sensors at the organ of interest;
monitoring parameters at another tissue of the patient continuously for a systemic reference, including at least NADH (NADHS) level and at least two parameters from among the group consisting of blood flow (BFS), blood hemoglobin (HbO2S), and tissue reflectance (TRS), and substantially continuously, computing a systemic vitality index from the monitored systemic parameters;
monitoring for a divergence in the temporal trend of the vitality index of the organ of interest from the systemic reference vitality index; and
based on the detection of the divergence, raising an alarm to a physician to warn the physician of a change in the patient's condition.
|