| CPC A61B 5/0215 (2013.01) [A61B 5/002 (2013.01); A61B 5/029 (2013.01); A61B 5/02028 (2013.01); A61B 5/686 (2013.01); A61B 5/7275 (2013.01); A61B 5/7282 (2013.01); G16H 20/10 (2018.01); G16H 50/20 (2018.01); A61B 5/02 (2013.01); A61B 2560/0219 (2013.01); A61B 2560/0228 (2013.01); A61B 2562/0247 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
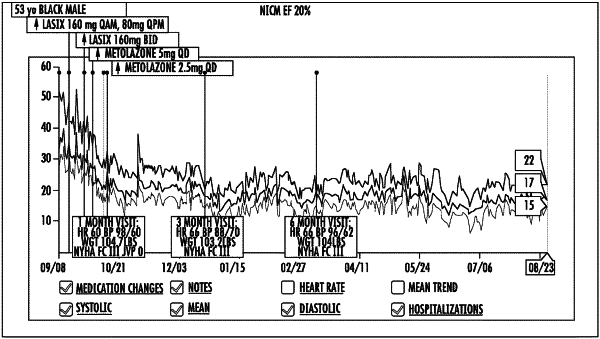
1. A method of evaluating progress of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) in a subject, or an outcome in the subject having PAH, comprising:
obtaining pulmonary artery pressure (PAP) data over a cardiac cycle from a wireless pressure sensor implanted in a pulmonary artery of the subject, the wireless pressure sensor wirelessly communicating with a base unit, the base unit communicating with a second computer;
utilizing a processor of at least one of the base unit or second computer for:
determining first and second PAP values experienced within the pulmonary artery based on the PAP data;
estimating first and second cardiac outputs (COs) based on the first and second PAP values experienced within the pulmonary artery over the cardiac cycle;
comparing the first and second PAP values and comparing the first and second COs;
monitoring a PAH progression or outcome in the subject based on the comparing of first and second PAPs and first and second COs; and
changing at least one of a pharmaceutical agent, dosage or dosing regimen based on the PAH progression or outcome in the subject.
|