| CPC H04N 23/11 (2023.01) [G01J 5/53 (2022.01); G01J 5/54 (2013.01); G01J 5/56 (2013.01); G01J 2005/0077 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
1. A process for simulating hyperspectral imaging data or multispectral imaging data for a simulated sensor for use in designing and testing infrared planetary observation systems, the process comprising:
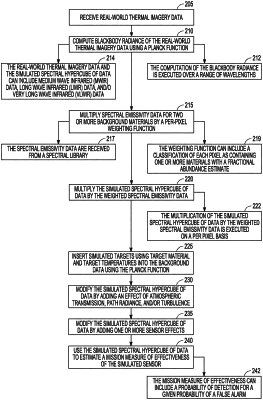
receiving into a computer processor real-world thermal imagery data and spectral emissivity for two or more background materials;
computing blackbody radiance of the real-world thermal imagery data using a Planck function, thereby generating a simulated spectral hypercube of data;
multiplying the spectral emissivity data for two or more background materials by a per-pixel weighting function, thereby generating weighted spectral emissivity data and a mixture of materials within a pixel;
multiplying the simulated spectral hypercube of data by the weighted spectral emissivity data, thereby generating background data in the simulated spectral hypercube of data;
inserting simulated targets using target material and target temperatures into the background data using the Planck function;
modifying the simulated spectral hypercube of data by adding one or more of an effect of atmospheric transmission, path radiance, and turbulence;
modifying the simulated spectral hypercube of data by adding one or more sensor effects comprising noise, a modular transfer function loss due to diffraction, a sampling of the simulated sensor, an optical aberration, a scanning of the simulated sensor, and a line-of-sight motion of the simulated sensor; and
using the simulated spectral hypercube of data to estimate a mission measure of effectiveness of the simulated sensor.
|