| CPC G06F 18/2135 (2023.01) [G06F 2218/12 (2023.01)] | 8 Claims |
|
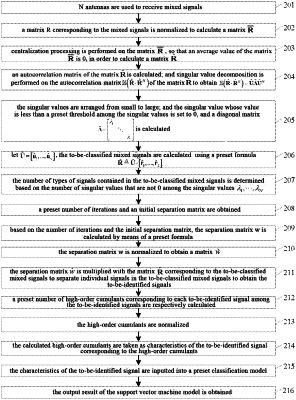
1. A method for classifying mixed signals, comprising:
receiving mixed signals containing noises and at least two different types of signals;
performing calculation on a matrix corresponding to the mixed signals by means of a preset Principal Component Analysis PCA method to obtain to-be-classified mixed signals and to determine the number of types of signals contained in the to-be-classified mixed signals; wherein the to-be-classified mixed signals are mixed signals obtained after removing the noises in the mixed signals;
determining a separation matrix based on the number of types of signals contained in the to-be-classified mixed signals;
separating individual signals in the to-be-classified mixed signals by means of the separation matrix to obtain to-be-identified signals;
calculating a preset number of high-order cumulants corresponding to each to-be-identified signal in the to-be-identified signals respectively;
taking the calculated high-order cumulants as characteristics of the to-be-identified signal corresponding to the high-order cumulants respectively;
inputting the characteristics of the to-be-identified signal into a preset classification model; wherein the classification model is used for calculating and outputting a modulation mode of the to-be-identified signal based on the characteristics of the to-be-identified signal; and
obtaining an output result of the classification model; wherein the output result comprises the modulation mode of the to-be-identified signal;
wherein performing calculation on the matrix corresponding to the mixed signals by means of the preset Principal Component Analysis PCA method to obtain to-be-classified mixed signals and to determine the number of types of signals contained in the to-be-classified mixed signals, comprises:
normalizing a matrix R corresponding to the mixed signals to calculate a matrix R; wherein the matrix R is a matrix obtained by normalizing the matrix R corresponding to the mixed signals;
performing centralization processing on the matrix R, so that an average value of the matrix R is 0, in order to calculate a matrix R;
calculating an autocorrelation matrix of the matrix R; performing singular value decomposition on the autocorrelation matrix
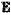 (R·R″) of the matrix R to obtain (R·R″) of the matrix R to obtain 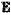 (R·R″)=ÛΛÛ″, wherein R″ is a transposed conjugate matrix of the matrix R, Û″ is a transposed conjugate matrix of Û, Û=[û1, . . . , ûN] is an orthogonal matrix, and ûN is a n-th column of the matrix Û, a diagonal matrix Λ is (R·R″)=ÛΛÛ″, wherein R″ is a transposed conjugate matrix of the matrix R, Û″ is a transposed conjugate matrix of Û, Û=[û1, . . . , ûN] is an orthogonal matrix, and ûN is a n-th column of the matrix Û, a diagonal matrix Λ is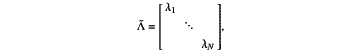 N is the number of antennas receiving the mixed signals; and λ1, . . . , λN are singular values of the autocorrelation matrix
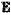 (R·R″; (R·R″;arranging the singular values λ1, . . . , λN from small to large; and setting singular values, whose numerical values are less than a preset threshold, among the singular values λ1, . . . , λN to 0, and calculating a diagonal matrix
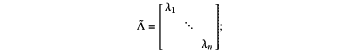 letting Ũ=[û1, . . . , ûN], calculating the to-be-classified mixed signals using a preset formula R≙Ũ·[rl, . . . , rL]; the matrix corresponding to the to-be-classified mixed signals is R; and
determining the number of types of signals contained in the to-be-classified mixed signals based on the number of singular values that are not 0 among the singular values λ1, . . . , λN.
|