| CPC G02F 1/212 (2021.01) [G02B 6/2935 (2013.01); G02F 1/0147 (2013.01); G02B 2006/12159 (2013.01)] | 17 Claims |
|
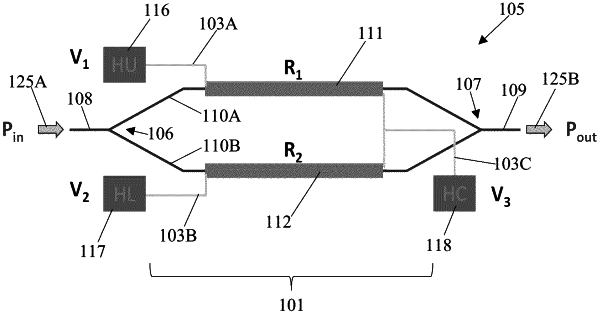
1. An integrated Mach-Zehnder Interferometer (MZI) comprising:
an upper arm and a lower arm; and
a differential thermo-optic phase shifter associated with the upper and the lower arms, the differential thermo-optic phase shifter comprising:
a first heating element and a second heating element collocated with the upper arm and the lower arm, respectively, the first heating element having a first resistance and the second heating element having a second resistance;
an upper pad electrically connected to the first heating element, the upper pad being adapted to receive a first voltage;
a lower pad electrically connected to the second heating element, the lower pad being adapted to receive a second voltage; and
a common pad electrically connected to the first heating element and the second heating element, the common pad being adapted to receive a third voltage;
wherein, the upper arm has a first thermally induced optical phase shift coefficient associated with the first heating element and the lower arm has a second thermally induced optical phase shift coefficient associated with the second heating element, and wherein, when the first and the second voltages are applied to the upper and the lower pads, respectively, and the third voltage is applied to the common pad, a phase shift difference is thermally produced between the upper arm and the lower arm, the phase shift difference being controlled by the applied third voltage and the first resistance and associated first thermally induced optical phase shift coefficient and the second resistance and associated second thermally induced optical phase shift coefficient are equal in value (R1=R2=R and KΦ1=KΦ2=KΦ), respectively.
|