| CPC E21B 49/0875 (2020.05) [E21B 49/081 (2013.01); G01N 33/2823 (2013.01)] | 17 Claims |
|
1. A method for downhole fluid analysis, comprising:
deploying a sampling system downhole in a borehole located within a reservoir containing oil;
using the sampling system to obtain samples of the oil at a plurality of stations along the borehole;
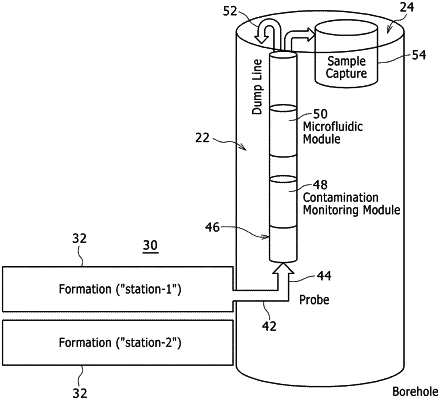
analyzing each sample of the oil in situ via a contamination monitoring module of the sampling system to obtain contamination data to correct for contamination of the oil resulting from the presence of a non-native reservoir fluid, wherein the contamination data is at least partially based on sensor data from a first viscosity sensor, a first density sensor, a first optical sensor, or a combination thereof, in the contamination monitoring module;
analyzing each sample of the oil in situ via a microfluidic measurement module of the sampling system to obtain, independent from the contamination data, a phase transition property of the oil having the contamination, wherein the phase transition property is at least partially based on sensor data from a depressurization chamber and at least one of a second density sensor, a second viscosity sensor, a second optical sensor, or a combination thereof, in the microfluidic measurement module; correcting the phase transition property with the contamination data to obtain a true phase transition property of the oil without the contamination in each sample of the oil; and
recirculating each sample of the oil through the contamination monitoring module and the microfluidic measurement module for iterative processing comprising the analyzing to obtain the contamination data, the analyzing to obtain the phase transition property, and the correcting to obtain the true phase transition property.
|