| CPC B01L 3/5027 (2013.01) [C12Q 1/6837 (2013.01); B01J 2219/00529 (2013.01); B01J 2219/00576 (2013.01); B01J 2219/00626 (2013.01); B01L 7/52 (2013.01); C12Q 1/6848 (2013.01); C12Q 1/6876 (2013.01); C12Q 2565/60 (2013.01); C12Q 2565/607 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
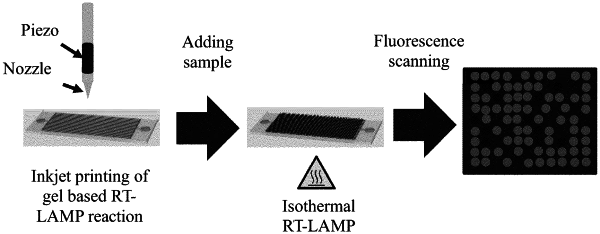
13. A method of preparing a biogel nanosensor comprising:
a) obtaining an acryloyl hydrogel or a methacryloyl hydrogel;
b) printing the hydrogel in picoliter or nanoliter volume on the surface of a substrate in a microarray in the form of spots;
c) crosslinking the hydrogel on the surface of the substrate; and
d) combining nucleic acid amplification reagents in picoliter or nanoliter volume to the cross-linked hydrogel.
|