| CPC H04L 9/3234 (2013.01) [H04L 9/002 (2013.01); H04L 9/3247 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
1. A method performed by hardware processing circuitry, the method
comprising:
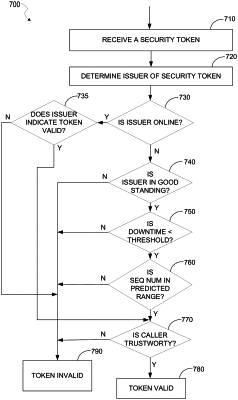
determining, from a plurality of notifications, a rate of change of a plurality of token sequence numbers, the rate of change indicating a number of increments or decrements of a baseline sequence number that occur per unit time, the increments or decrements increase or decrease the baseline sequence number by a determinable amount;
receiving a first security token at a first time, the first security token including a token sequence number;
responsive to determining an issuer of the first security token is offline, determining, based on the first time and the rate of change, a token sequence number confidence interval of the issuer; and
validating, based on determining the token sequence number included in the first security token is within the token sequence number confidence interval, the first security token.
|