| CPC H04L 63/1416 (2013.01) [B60R 16/0231 (2013.01); H04L 12/28 (2013.01); H04L 63/1425 (2013.01); H04L 67/12 (2013.01); H04L 2012/40215 (2013.01); H04L 2012/40273 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
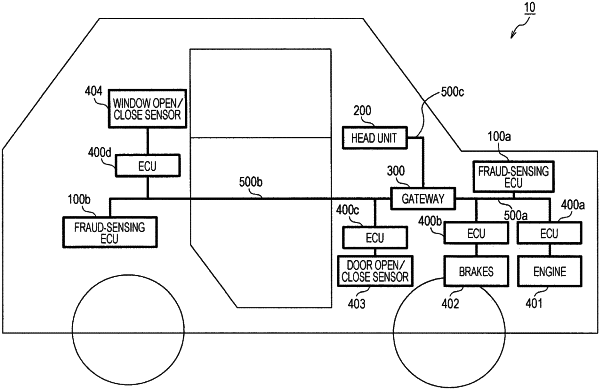
1. A fraud message detecting method for use in an in-vehicle network system, the in-vehicle network system including a plurality of first electronic control units that communicate with each other via one or more networks, the fraud message detecting method comprising:
detecting whether a state of a vehicle including the in-vehicle network system satisfies a first condition or a second condition; and
switching an operation mode of a second electronic control unit connected to the one or more networks:
from a first mode in which a first type of detecting process for detecting a fraudulent message in the one or more networks is performed to a second mode in which the first type of detecting process is not performed, upon detecting, in the detecting, that the state of the vehicle satisfies the first condition; and
from the second mode to the first mode, upon detecting, in the detecting, that the state of the vehicle satisfies the second condition,
wherein, in the second mode, a second type of detecting process having a different degree to which a fraudulent message is detectible than the first type of detecting process is performed,
in the switching, the switch from the first mode to the second mode occurs when no fraudulent message is detected for a predetermined time, and
the second mode is a standby mode.
|