| CPC H04L 63/10 (2013.01) [G06F 40/117 (2020.01); G06F 40/289 (2020.01); G06N 20/00 (2019.01); G06Q 10/107 (2013.01)] | 17 Claims |
|
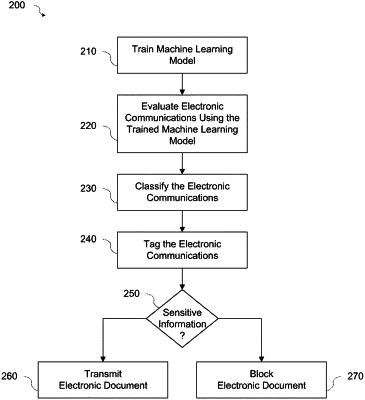
1. A computer-implemented method comprising:
evaluating, by a machine-learning model trained using historical electronic communications, content of an electronic communication that is attempted to be transmitted from a first network having a first security level by reading in the content to the machine-learning model, identifying by the machine-learning model a predetermined number of words or phrases or both in the content indicating that the electronic communication contains specific information that the machine-learning model is trained to recognize and a confidence score indicating a degree of confidence that the specific information is contained in the electronic communication;
determining that the specific information recognized by the machine-learning model contained in the electronic communication requires transmission on a network having at least the first security level;
tagging the electronic communication with tag information specifying a classification for at least the first security level indicating that the electronic communication contains the specific information recognized by the machine-learning model and including the confidence score;
determining whether the confidence score exceeds a predetermined threshold;
determining a security level of a second network for receiving the electronic communication; and
based on the tag information and in response to determining that the confidence score exceeds the predetermined threshold, blocking attempted transmission of the electronic communication from the first network to a second network when the second network has a second security level lower than the first security level.
|