| CPC H01M 8/04952 (2016.02) [H01M 8/0488 (2013.01); H01M 8/0491 (2013.01); H01M 8/0494 (2013.01); H01M 8/04134 (2013.01); H01M 8/04708 (2013.01); H01M 8/04753 (2013.01); H01M 2250/20 (2013.01)] | 5 Claims |
|
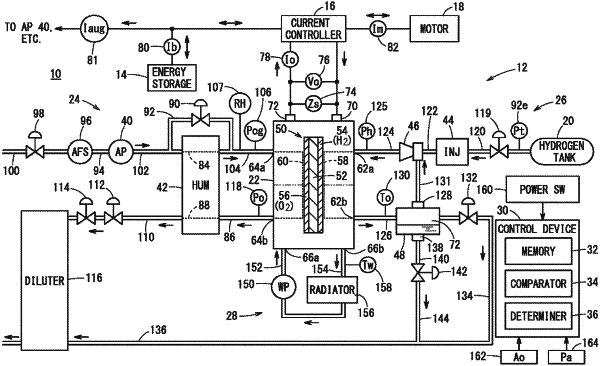
1. A method of determining degradation of a solid polymer electrolyte fuel cell stack located on a vehicle, wherein the fuel cell stack includes a plurality of power generation cells stacked together, the power generation cells being each configured to perform power generation by electrochemical reactions of a fuel gas and an oxygen-containing gas, the method comprising:
storing, by a device comprising a processor, output characteristics of an initial state of the fuel stack as a reference value;
measuring, by the device, each of a pressure of the oxygen-containing gas supplied to the fuel cell stack, a flow rate of the oxygen-containing gas supplied to the fuel cell stack, a temperature of the fuel cell stack, an impedance of the fuel cell stack, an output current of the fuel cell stack, and an output voltage of the fuel cell stack;
comparing, by the device, each of the measured pressure of the oxygen-containing gas supplied to the fuel cell stack, the measured flow rate of the oxygen-containing gas supplied to the fuel cell stack, the measured temperature of the fuel cell stack, the measured impedance of the fuel cell stack, the measured output current of the fuel cell stack, and the measured output voltage of the fuel cell stack, with a predetermined range;
in response to determining that, only in a case where each of the measured pressure of the oxygen-containing gas supplied to the fuel cell stack, the flow rate of the oxygen-containing gas supplied to the fuel cell stack, the measured temperature of the fuel cell stack, the measured impedance of the fuel cell stack, the measured output current of the fuel cell stack falls within the predetermined range, comparing, by the device, the measured output voltage of the fuel cell stack with the-reference value to facilitate determining, by the device, a degree of degradation of the fuel cell stack;
measuring, by the device, an atmospheric pressure; and
only in a case where each of the measured pressure of the oxygen-containing gas supplied to the fuel cell stack, the measured flow rate of the oxygen-containing gas supplied to the fuel cell stack, the temperature of the fuel cell stack, the impedance of the fuel cell stack, and the output current of the fuel cell stack, and the measured atmospheric pressure falls within a predetermined range, a measurement value of the output voltage of the fuel cell stack is determined, by the device.
|