| CPC G06Q 10/063 (2013.01) [G06F 17/18 (2013.01); G06F 18/2321 (2023.01); G06F 18/2415 (2023.01); G06N 7/02 (2013.01); G06Q 10/04 (2013.01); G06Q 10/087 (2013.01); G06T 7/0002 (2013.01); G06V 20/52 (2022.01); G06T 2207/30242 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
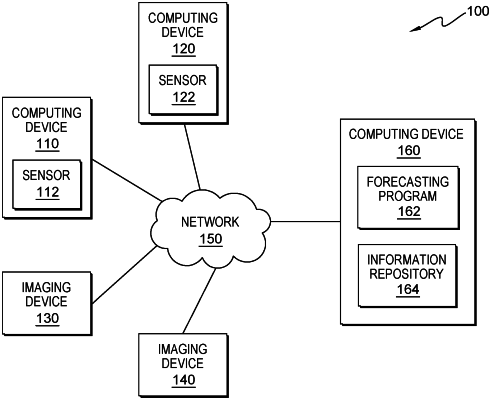
|
1. A computer-implemented method comprising:
receiving, by one or more computer processors, first data compiled remotely from a plurality of Internet of Things (IoT) sensors located at multiple disparate food store locations throughout a geographic area, wherein the plurality of IoT sensors:
collects data comprising food item temperature, relative humidity, food item moisture content; and
includes a gas sensor that collects data including food item gas emissions;
determining, by one or more computer processors, an amount and condition of food available throughout the geographic area based on the first data, wherein the condition of the food is determined based on, at least, food item gas emission data;
determining, by one or more computer processors, a number and location of people throughout the geographic area based on the first data;
modifying, by one or more computer processors, the first data to create second data;
predicting, by one or more computer processors, one or more food requirements for the people based on the number and location of people and the second data;
predicting, by one or more computer processors, an optimal food allocation for the people based on the amount and condition of food available and the one or more food requirements;
reporting, by one or more computer processors, the optimal food allocation;
determining, by one or more computer processors, a probability that one or more people of the people will run out of food based on the amount and condition of food available and the one or more food requirements; and
responsive to the probability of any of the one or more people being greater than a threshold, reporting, by one or more computer processors, a first group of people of the one or more people, wherein the first group of people have the probability greater than the threshold.
|