| US 11,810,009 B2 | ||
| Methods of explaining an individual predictions made by predictive processes and/or predictive models | ||
| Gregory Dean Jorstad, Draper, UT (US); and Thomas Patrick Prendergast, Jr, Draper, UT (US) | ||
| Assigned to Synchrony Bank, Stamford, CT (US) | ||
| Filed by Synchrony Bank, Stamford, CT (US) | ||
| Filed on Sep. 7, 2022, as Appl. No. 17/930,076. | ||
| Application 17/930,076 is a continuation of application No. 16/293,407, filed on Mar. 5, 2019, granted, now 11,475,322. | ||
| Prior Publication US 2023/0109251 A1, Apr. 6, 2023 | ||
| Int. Cl. G06N 5/04 (2023.01); G06N 20/00 (2019.01); G06F 3/14 (2006.01) | ||
| CPC G06N 5/04 (2013.01) [G06N 20/00 (2019.01); G06F 3/14 (2013.01)] | 21 Claims |
|
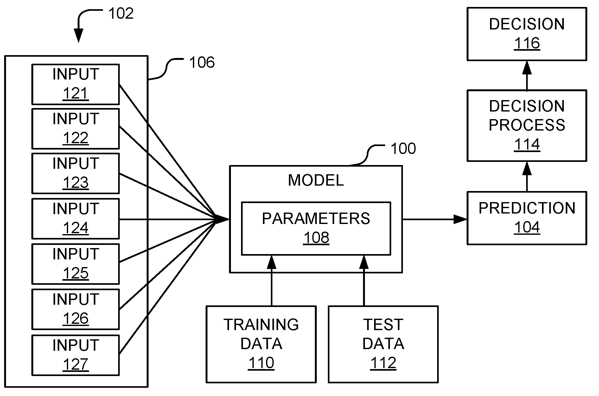
1. A computer-implemented method comprising:
receiving an input record on an explanation computing device, wherein the explanation computing device includes an input message broker, a model executing engine, one or more sample bins, an explanation live process, and an output message broker, wherein the input record includes a set of input variables and a set of values corresponding to the set of input variables, and wherein the input record is received through the input message broker; generating an actual prediction by processing the input record using the model executing engine; generating a set of modified input records, wherein the set of modified input records are generated by the explanation computing device, wherein a modified input record is generated by modifying a particular value associated with a particular input variable without modifying other values associated with other input variables, and wherein the particular value is modified using a set of sample values obtained from the one or more sample bins; generating a set of sample predictions by processing the set of modified input records using the model executing engine; executing the explanation live process to evaluate the set of sample predictions against the actual prediction to identify an influential input variable; and providing a justification for identification of the influential input variable through the output message broker, wherein the justification includes sample predictions corresponding to changes to influential input variable values. |